The global shift toward electric vehicles (EVs) is accelerating faster than ever. Governments, automakers, and consumers are embracing EVs as a cleaner alternative to internal combustion engine vehicles. However, as millions of electric cars hit the roads, a critical question arises: What happens to EV batteries at the end of their life?
This is where EV battery recycling becomes essential. Understanding the EV battery recycling process is crucial for sustainability, resource conservation, environmental protection, and long-term economic growth. This in-depth guide explains how EV batteries are recycled, why the process matters, and how it supports the future of clean transportation.
What Is an EV Battery and Why Recycling Is Important
Electric vehicles primarily use lithium-ion batteries, which contain valuable and finite materials such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, manganese, copper, aluminum, and graphite. These batteries are designed to last between 8 to 15 years, depending on usage and environmental conditions.
When an EV battery reaches the end of its automotive life, it may no longer meet performance requirements, but it still contains recoverable materials. Recycling ensures that these resources are reused instead of being discarded.
Key Reasons EV Battery Recycling Matters
-
Resource conservation: Reduces dependence on mining raw materials
-
Environmental protection: Prevents soil and water contamination
-
Energy efficiency: Recycling uses less energy than raw material extraction
-
Economic value: Creates a circular economy for battery materials
-
Regulatory compliance: Meets environmental and safety regulations
Lifecycle of an EV Battery Before Recycling
Before entering the recycling stream, EV batteries go through multiple stages:
-
Active vehicle use
-
Performance degradation
-
Second-life applications
-
End-of-life recycling
Many batteries are repurposed for stationary energy storage, such as solar or grid backup systems, before being recycled.
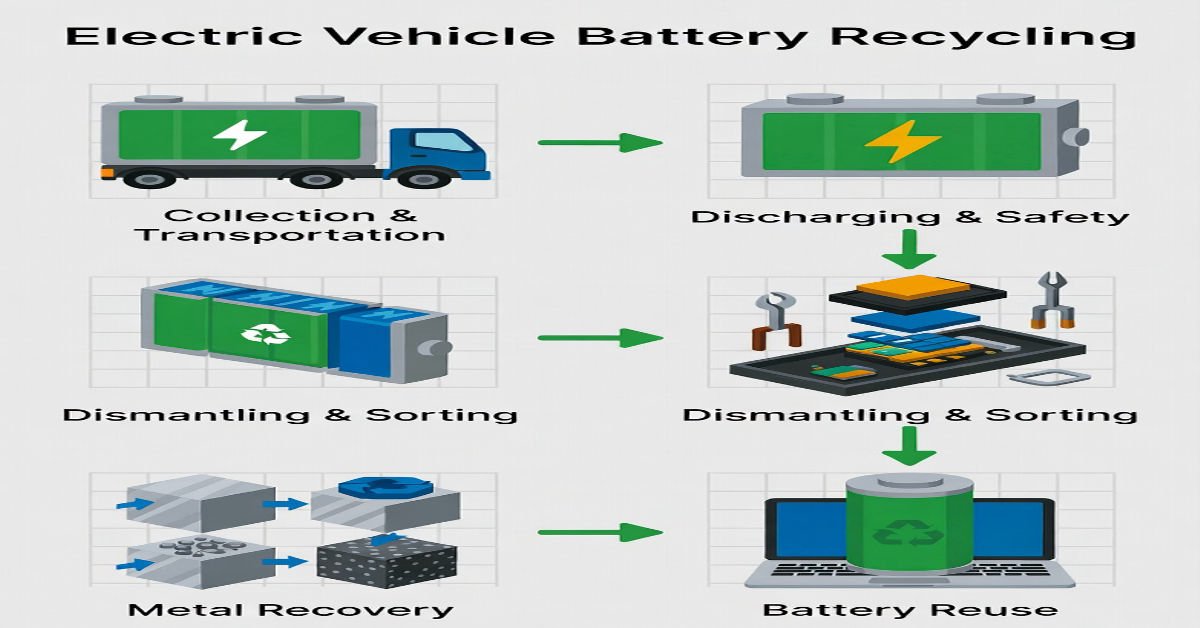
Overview of the EV Battery Recycling Process
The EV battery recycling process is complex and highly controlled due to safety, chemical, and environmental considerations. Below is a simplified overview:
| Stage | Purpose | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Collection & Transport | Safe handling of used batteries | Prevents fire and leakage |
| Discharging | Eliminates stored energy | Improves safety |
| Dismantling | Separation of components | Enables material recovery |
| Processing | Chemical or thermal treatment | Extracts valuable metals |
| Refinement | Purification of materials | Ready for reuse in batteries |
Each stage plays a critical role in ensuring safe, efficient, and environmentally responsible recycling.
Step 1: Collection and Safe Transportation
The first step in EV battery recycling involves collecting used batteries from:
-
Electric vehicles
-
Fleet operators
-
Dealerships
-
Recycling centers
-
Energy storage systems
Because lithium-ion batteries can pose fire and explosion risks, transportation follows strict safety standards. Batteries are stored in insulated containers and tracked digitally to ensure compliance.
Step 2: Battery Discharging and Stabilization
Before dismantling, batteries must be fully discharged. Even degraded batteries can retain significant electrical energy, making them dangerous to handle.
Specialized systems safely neutralize residual charge and stabilize the battery. This step significantly reduces the risk of:
-
Short circuits
-
Thermal runaway
-
Fires during dismantling
Step 3: Dismantling and Mechanical Separation
After stabilization, batteries are manually or mechanically dismantled. This stage involves:
-
Removing battery packs from casings
-
Separating modules and cells
-
Extracting plastics, wiring, and electronics
Materials Recovered at This Stage
| Component | Recovered Material | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Casing | Aluminum, steel | New vehicle parts |
| Wiring | Copper | Electrical systems |
| Plastics | Polymers | Industrial reuse |
Mechanical separation increases efficiency in later processing stages.
EV Battery Recycling Methods Explained
There are three primary EV battery recycling methods currently in use. Each has advantages and limitations.
1. Pyrometallurgical Recycling (High-Temperature Method)
This method uses extreme heat to melt battery components and extract metals.
Process Explanation
-
Batteries are placed in industrial furnaces
-
High temperatures burn off plastics and electrolytes
-
Metals such as cobalt, nickel, and copper are recovered
Advantages
-
Proven and widely used
-
Handles mixed battery chemistries
-
Robust and scalable
Limitations
-
High energy consumption
-
Loss of lithium and aluminum
-
Higher carbon emissions
2. Hydrometallurgical Recycling (Chemical Leaching Method)
Hydrometallurgy uses chemical solutions to dissolve and separate metals.
Process Explanation
-
Batteries are shredded into fine particles
-
Chemical leaching extracts metals
-
Metals are purified through precipitation
Advantages
-
High recovery rate (up to 95%)
-
Lower energy usage
-
Better lithium recovery
Limitations
-
Chemical waste management required
-
More complex processing
3. Direct Recycling (Emerging Technology)
Direct recycling aims to preserve battery materials in their usable form.
Process Explanation
-
Cathode materials are separated intact
-
Materials are reconditioned instead of broken down
-
Reused directly in new batteries
Advantages
-
Highest sustainability potential
-
Lower processing cost in future
-
Preserves material structure
Limitations
-
Still under development
-
Requires standardized battery designs
Comparison of EV Battery Recycling Methods
| Method | Recovery Rate | Energy Use | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrometallurgy | Medium | High | Moderate to High |
| Hydrometallurgy | High | Medium | Lower |
| Direct Recycling | Very High | Low | Minimal |
Material Refinement and Reuse
Once materials are recovered, they undergo purification to meet battery-grade standards. Recycled metals are then supplied back into the battery manufacturing supply chain.
Common Reused Materials
-
Lithium → New EV batteries
-
Cobalt → Cathode materials
-
Nickel → High-energy batteries
-
Copper → Electrical components
This circular approach significantly reduces mining demand and environmental damage.
Environmental Benefits of EV Battery Recycling
EV battery recycling plays a vital role in reducing the environmental footprint of electric mobility.
Major Environmental Advantages
-
Reduces greenhouse gas emissions
-
Prevents toxic waste leakage
-
Conserves water and land resources
-
Lowers dependence on mining operations
Recycling one ton of lithium-ion batteries can save thousands of kilograms of raw material extraction.
Economic and Social Impact of EV Battery Recycling
Beyond environmental gains, battery recycling creates economic opportunities.
Economic Benefits
-
Job creation in recycling facilities
-
Reduced battery production costs
-
Strengthened domestic supply chains
Social Benefits
-
Safer waste management
-
Reduced mining-related conflicts
-
Cleaner communities
Global Regulations and EV Battery Recycling Policies
Many countries are introducing strict regulations to ensure responsible battery disposal and recycling.
| Region | Policy Focus | Key Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| European Union | Extended Producer Responsibility | Mandatory recycling targets |
| United States | State-level programs | Safe disposal standards |
| China | Producer accountability | Battery tracking systems |
| India | E-waste management rules | Authorized recyclers only |
These policies encourage automakers to design batteries with recyclability in mind.
Challenges in the EV Battery Recycling Process
Despite progress, challenges remain:
-
Lack of battery design standardization
-
High initial investment costs
-
Limited recycling infrastructure
-
Transportation safety concerns
Ongoing innovation and regulatory support are addressing these issues.
Future of EV Battery Recycling
The future of EV battery recycling is promising. Advancements in technology, automation, and battery design will improve efficiency and sustainability.
Emerging Trends
-
AI-driven sorting systems
-
Battery-to-battery recycling
-
Modular battery designs
-
Closed-loop manufacturing
As EV adoption grows, recycling will become a core pillar of the clean energy ecosystem.
Conclusion: Why EV Battery Recycling Matters for a Sustainable Future
The EV battery recycling process is not just an environmental necessity—it is a strategic solution for sustainable transportation, resource security, and economic resilience. By recovering valuable materials and reducing waste, recycling ensures that electric vehicles truly remain a green alternative.
As technology improves and global cooperation increases, EV battery recycling will play a decisive role in shaping a cleaner, more responsible future for mobility.
1 thought on “EV Battery Recycling Process Explained”